Citing financial struggles, 54.2% of universities hike fees
Input
Modified
In 2009, South Korea implemented a tuition fee moratorium that was effectively mandatory for universities. Institutions that attempted to increase fees were subject to financial penalties to enforce this policy. The University of Seoul implemented the "half-price" tuition policy in 2012, which served to further solidify this policy. The tuition fee freeze and halving significantly reduced the university's annual cost to approximately 2.4 million won ($1,820), which is under the jurisdiction of the Seoul Metropolitan Government. This figure is substantially less than the national average of 6.8 million won. The policy was initially designed to alleviate the financial burdens on students; however, it has led to substantial financial challenges for universities. Numerous institutions argue that their capacity to improve facilities, recruit top-tier faculty, and allocate resources to research and development has been impeded by stagnant tuition fees. Universities are presently assessing tuition increases as a means of sustaining operations, as government funding remains insufficient. Furthermore, the learning environment has been negatively impacted, and research output has been reduced as a consequence of outdated educational infrastructure and insufficient financial resources.
The protracted tuition moratorium has resulted in significant financial strain for both national and private universities. Over 80% of South Korean pupils are enrolled in private institutions, which receive minimal government funding. Universities have been unable to increase tuition, which has exacerbated financial deficits. The cumulative tuition revenue of private universities outside Seoul decreased by 7.9% from 2010 to 2020, while universities in Seoul only experienced a 3% increase.
The moratorium has a substantial effect on the efficiency of universities and the quality of professors. The potential decline in academic standards has been a cause for concern among many institutions, as they have faced challenges in recruiting and retaining high-quality faculty members due to financial constraints. Additionally, the education system has been further encumbered by budget cuts, which have led to a reduction in research funding, faculty development programs, and campus maintenance. Ultimately, the quality of instruction and student learning experiences have been influenced by the heightened burdens and reduced resources that professors have encountered. The capacity of universities to contribute to global academic advancements and to innovate has been restricted as a result of the increased teaching responsibilities that have been taken on by a significant number of faculty members at the expense of conducting research.

In addition, universities have reported difficulties in attracting international scholars by providing competitive salaries, upgrading laboratory apparatus, and modernizing facilities. These constraints have led to a brain outflow, as talented academicians have opted to pursue positions at institutions with greater funding or abroad. Students have responded by expressing their dissatisfaction with the outdated curriculum and the deteriorating campus conditions, which are not in accordance with global industry trends.
Tuition fees are anticipated to rise at 103 out of 190 four-year universities (54.2%), according to a recent report by the Korean Association of Private University Presidents. 94 out of 151 private institutions (62.3%) have also chosen to increase tuition, while nine out of 39 public universities (23.1%) are also doing so. For example, Yonsei University will raise undergraduate fees by nearly 5%, graduate fees by 5.2%, and international student fees by 6.5% after a 15-year moratorium. Other institutions, including Kyung Hee University (5.1%) and Korea University (5.0%), are approaching the legal tuition increase limit of 5.49% mandated by the Higher Education Act.

Despite the financial constraints that universities are currently experiencing, students have consistently voiced their opposition to tuition increases. 96% of the 3,800 respondents who participated in a survey conducted by the Yonsei University Student Council rejected the proposed increases. According to the survey conducted at Hongik University, 94.2% of the students were opposed to the increases, citing concerns that the quality of education would not necessarily improve as a result of the higher fees. Student leaders argue that universities should alter their financial models rather than placing the burden on students and their families. Furthermore, students have expressed their frustration with the university's financial management as a result of its lack of transparency. There are numerous individuals who argue that universities should prioritize the optimization of their current budgets and the reduction of unnecessary administrative expenses, rather than the increase in tuition. In recent years, student organizations have been advocating for heightened government intervention to provide higher education institutions with more substantial funding, as protests against tuition increases have intensified. In an effort to reduce tuition fees, certain organizations have also proposed alternative financing models, such as corporate partnerships and alumni donation programs.
In an effort to discourage universities from raising tuition, the South Korean government has offered financial incentives to those that maintain the moratorium. The Private University Restructuring Act would facilitate the conversion of financially distressed universities into social welfare organizations or non-profits, while the proposed Higher Education Finance Grant Act is designed to guarantee consistent funding for institutions that are grappling with financial challenges.
South Korea is not the sole nation that is grappling with a tuition crisis. In Japan, there has been a surge in discussions about tuition fee increases, particularly at the University of Tokyo, which has proposed an increase to maintain its competitive edge. National universities have been permitted to establish their tuition fees within ministerial guidelines as independent corporate entities since the 2004 reforms. However, the public and students have consistently voiced their opposition to any increase.
Critics of tuition increases in Japan argue that the escalation of fees will exacerbate inequalities and limit access to higher education, particularly for students from low-income backgrounds. Conversely, proponents contend that tuition increases are indispensable for enhancing institutional competitiveness and preserving the quality of education in the global academic environment. In response to an aging population and a declining student body, universities in Japan are also exploring innovative methods to secure funding, such as government-endorsed financial aid programs and strategic partnerships with international institutions.

The financing of universities is further complicated by the current demographic crises in South Korea and Japan, which are characterized by declining birth rates and diminishing student populations. The enrollment shortage in South Korea has been a consequence of the fact that the number of pupils has surpassed the number of university spaces since 2020. Experts predict that South Korea will require approximately 40 universities of the current magnitude by 2038. This raises serious concerns about the criteria for determining which institutions should remain open and how they should be distinguished.
In both countries, tuition policies remain a contentious issue, and governments, universities, and students are still grappling with the challenge of maintaining financial sustainability while ensuring an accessible, high-quality education. In the absence of long-term financing reforms, the sustainability of higher education in South Korea and Japan is uncertain. To confront these obstacles, a multifaceted strategy will be required. This strategy will encompass policies that are intended to improve financial planning at the university level, increase public investment, and revitalize student enrollment in the context of demographic decline.
Similar Post
Students have been sold a dream by agents and universities
Input
Modified
Many countries have implemented policies to attract international students for their financial and intellectual contributions, as international education has become a propelling force in global mobility and economic strategy. This has resulted in the emergence of exploitative recruitment agencies and fraudulent institutions that exploit the demand for overseas education, despite the fact that it presents valuable opportunities for both students and host nations. Although legitimate agencies offer crucial assistance in traversing intricate visa and enrollment procedures, unethical actors deceive students by making false claims about guaranteed visas, employment, and residency. This absence of supervision not only compromises the credibility of educational institutions but also positions international students in precarious emotional and financial circumstances. To guarantee that students are afforded the opportunities they desire, and that international education maintains its integrity, it is imperative to establish more stringent regulations, enhance institutional accountability, and establish comprehensive support systems. International education is at risk of becoming more of an immigration loophole than a pathway to genuine academic and professional development in the absence of these measures.

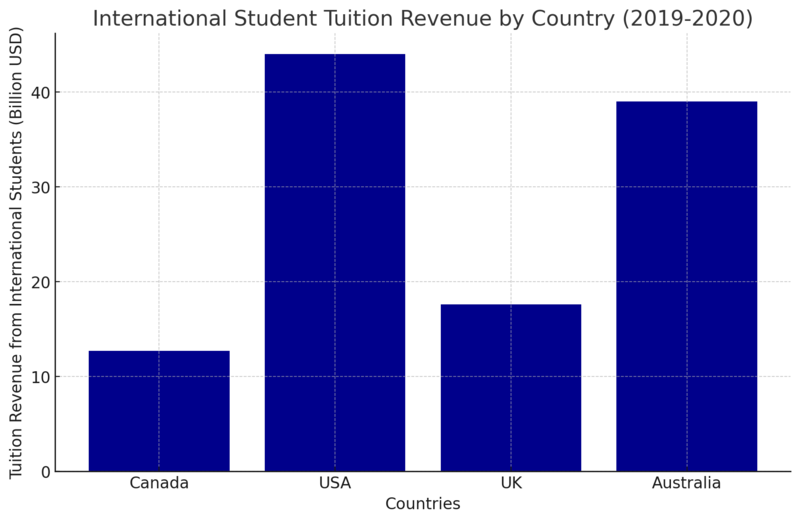
Countries such as the United States, Canada, Australia, and the United Kingdom are actively competing for international students, primarily due to the economic benefits. In order to compensate for diminished public funding, universities and colleges significantly depend on tuition from foreign students. In 2019-2020, tuition fees from international students in Canada generated an estimated $12.7 billion. An inundation of recruitment agencies has resulted from this financial incentive, which is exploiting students' urge to migrate. According to a 2021 audit report, approximately 280,000 international students were enrolled in Ontario, accounting for 68% of college tuition revenue. These institutions are susceptible to market fluctuations, visa policy modifications, and recruitment fraud due to their financial dependence on foreign students. Studying abroad is not merely an academic endeavor for numerous international students; it is also a means of obtaining employment and residency. For instance, Canada's immigration system offers graduates of Canadian institutions the opportunity to earn additional points when applying for permanent residency. Nevertheless, this system has resulted in agents who deceive students into believing that enrollment in particular institutions guarantee immigration.
Immigration agencies are essential in assisting students and laborers in navigating the intricate visa and settlement processes. They provide support in the areas of language requirements, documentation, and enrollment in educational institutions. Unfortunately, some agencies have engaged in deceptive practices, making false promises regarding visas, employment, and permanent residency. Concerns regarding fraudulent immigration agencies that fail to fulfill their obligations are underscored in a Quora thread. The majority of contributors concur that these actions are fraudulent and emphasize the importance of conducting thorough research prior to utilizing these services. The importance of appropriate supervision and regulation is underscored by the numerous individuals who have experienced fraud.
A substantial scandal has recently surfaced in Los Angeles, where the administrators of four schools were apprehended for operating a "pay-to-stay" scheme that enabled foreign nationals to maintain their student visa status without attending classes. The fraudulent institutions permitted students to remain in the United States without satisfying academic requirements by accepting tuition payments in exchange for Form I-20s. Three individuals were indicted for money laundering and immigration fraud, with a single school alone generating nearly $6 million annually from such schemes. This case demonstrates the potential for systemic abuse to result from inadequate governance, which can compromise the integrity of immigration and educational standards. In India and China, pupil recruitment malpractices have been identified through investigations. Billboards and advertisements in Punjab, India, advertise studying in Canada as a guaranteed route to permanent residency. Some agencies deceive families into selling assets to finance their children's overseas education by promising high-paying employment beyond graduation. Furthermore, it is purported that certain recruiters pay commissions to secure student placements, which frequently results in the exaggeration of application numbers. This has resulted in institutions prioritizing revenue over educational quality, resulting in admission offices that are overcrowded and academic standards that are diluted.
Many students who arrive under false pretenses are unable to fulfill academic obligations because of language barriers and employment responsibilities. Some individuals lack the requisite skills for higher education, despite successfully passing language proficiency examinations. Educators' reports indicate that the quality of education is compromised to facilitate students who are not adequately prepared. Additionally, students who anticipate lucrative employment opportunities frequently discover themselves employed in low-wage industries to maintain their financial stability. These students are exploited by businesses as cheap labor, while financial hardship compels them to pursue additional employment illegally. The high cost of living in Brampton, Ontario has resulted in a significant number of international students residing in illicit, overcrowded housing. In 2019, the city received 1,600 complaints concerning secondary housing units that were not regulated. The financial ruin that families who invested heavily in education-abroad dreams confront is a topic that is frequently discussed on Punjabi-language radio, with many callers emphasizing the issue. International students endure an immense mental health burden. A Toronto funeral home director has reported that they are responsible for the care of four to five international students' fatalities each month, which are believed to be the result of suicides or overdoses.

The challenges that students encounter have been largely disregarded by authorities, despite the fact that immigration agencies and educational institutions benefit from the system. Policy recommendations include the decoupling of education from immigration to ensure that admission to colleges is not a guaranteed pathway to residency. Rather, international graduates should be assessed in conjunction with other immigration applicants. To prevent fraudulent recruitment, immigration and education agents should be subject to more stringent licensing requirements and oversight. Regular academic audits can be implemented to guarantee that students remain enrolled full-time and attend legitimate institutions. To mitigate their dependence on international tuition, universities and colleges should receive sufficient government funding. Additionally, to guarantee the success of international students, universities must offer enhanced academic, employment, and mental health support.
The intersection of international education and immigration presents both opportunities and challenges. While students strive for academic and professional development, their aspirations are endangered by unethical recruitment practices and fraudulent institutions. To preserve the integrity of both the education and immigration systems, governments must establish a balance between economic benefits. The prioritization of transparency, ethical recruitment, and meaningful student support is essential for a fair and sustainable immigration policy. International education can only then fulfill its genuine purpose of promoting global knowledge exchange, rather than serving as a trivial entryway for migration.
Similar Post
How Universities Justify Their Massive Advertising Budgets
Input
Modified
Universities, particularly private and for-profit institutions, spend millions on advertising to attract students, justifying it through tuition revenue and increased competition While elite institutions rely on reputation, mid-tier and online schools depend on aggressive marketing to stay competitive The sustainability of high marketing expenditures is debated, as some institutions struggle to balance costs with enrollment revenue
Higher education institutions in the United States collectively spend billions on advertising. Reports indicate that major universities allocate $1–2 million per month on digital marketing alone. This spending encompasses online ads, search engine marketing, social media campaigns, and traditional media placements.
For example, Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) and Western Governors University (WGU) reportedly spend over $100 million per year on advertising. This raises a critical question: Is this money justified?

The Justification: Tuition Revenue vs. Marketing Costs
Most universities justify their advertising spend through tuition revenue. With tuition fees ranging from $10,000 to $50,000 per year, acquiring just a few hundred students through aggressive marketing can generate significant revenue.
- Return on Investment (ROI): If an online program costs $20,000 per student and the university spends $2,000 per student acquisition, they still net $18,000 per student.
- For-Profit Institutions: Schools like University of Phoenix and DeVry operate under a business model, where aggressive advertising ensures consistent student intake and profitability.
- Public Universities: State-funded schools also invest in marketing to secure government funding, as more students mean higher federal and state subsidies.
Advertising Strategies Used by Universities
To maximize visibility and enrollment numbers, universities deploy multiple advertising strategies:
- Digital Advertising:
- Google Ads and Facebook campaigns target prospective students searching for degree programs.
- Retargeting strategies ensure that users who visit a university's website continue seeing ads later.
- Social Media Influencers:
- Some institutions collaborate with student influencers to enhance their brand image and reach younger demographics.
- Traditional Media:
- Billboards, television commercials, and print ads in education-focused publications remain part of many universities' strategies.
- Email Marketing & Webinars:
- Direct outreach campaigns and virtual events help engage prospective students and convert leads into enrollments.
- Scholarship & Financial Aid Promotions:
- Many schools use scholarship offerings as a marketing tool, positioning their programs as affordable to entice students.
The Role of Increased Competition
Another major driver behind high marketing budgets is competition.
- The shrinking number of college-age students has intensified the race for enrollments.
- Online programs have blurred regional boundaries, forcing universities to compete globally.
- Traditional nonprofit universities are now competing with bootcamps, online certifications, and alternative education platforms, making visibility crucial.
Are Universities Profitable?
Despite high tuition revenue, profitability varies depending on the type of institution.
- Elite Institutions (Harvard, Stanford, MIT) – They rely on reputation, endowments, and research funding rather than advertising.
- Private Nonprofits (Small Liberal Arts Colleges) – Many struggle financially despite tuition revenue, leading some to close permanently.
- For-Profit Universities (University of Phoenix, DeVry) – These schools rely on volume-based enrollments, and advertising is essential for sustaining revenue.
The Debate: Is This Spending Sustainable?
The sustainability of high ad spending remains a debated issue.
- For elite universities? No need. Harvard and MIT have strong brand recognition.
- For mid-tier and online schools? Necessary. They must attract students aggressively.
- For struggling universities? Questionable. Some institutions spend more on ads than they recoup in tuition, leading to financial instability.
Additionally, the increasing skepticism toward higher education—with rising tuition costs and student debt concerns—raises questions about whether students will continue to enroll at the same rate in the future. Universities may need to rethink their models, focusing more on affordability, program flexibility, and real-world outcomes rather than pure advertising spend.
The Future of University Marketing
Looking ahead, universities may shift their focus toward more sustainable marketing models. Emerging trends include:
- AI-Driven Personalization: Leveraging artificial intelligence to tailor marketing content to individual student preferences.
- Content Marketing & Thought Leadership: Universities publishing research and expert analysis to organically attract students.
- Corporate Partnerships: Institutions aligning with businesses to offer industry-aligned degrees that appeal to working professionals.
- Lower-Cost Digital Strategies: Reducing reliance on expensive PPC (pay-per-click) campaigns and focusing more on organic growth.
University marketing budgets have skyrocketed in recent years, with some institutions spending over $100 million annually on advertising. While the investment often pays off in tuition revenue, the long-term sustainability is uncertain. As higher education evolves, institutions must balance aggressive marketing with financial viability to ensure they remain competitive without overspending.
In an era where student demographics are shifting and alternative education models are gaining traction, universities must adopt smarter, more cost-effective strategies. The schools that succeed will not necessarily be those that spend the most but rather those that adapt best to the changing landscape of higher education.
Similar Post
DeepSeek success puts focus on China’s universities
Input
Modified
A significant change in how Chinese colleges view their own capabilities has been sparked by DeepSeek's rise to prominence as a global AI powerhouse. Chinese colleges are now proving that they can generate top-tier innovators who compete at the highest levels—without having to leave the country—instead of being perceived as needing to send their brightest minds abroad for further education and research possibilities.

1. Homegrown Talent Is Driving Innovation
The foundation of DeepSeek's success is its research and development staff, which is primarily made up of recent graduates from Chinese universities, such as Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Tsinghua University, Peking University, and Zhejiang University. DeepSeek's core team members have received all of their training within China's academic system, in contrast to earlier generations of Chinese tech innovators who frequently studied overseas before making noteworthy contributions. Their accomplishments show that China's best universities have advanced to the point where they can develop the talent required to match or even outperform their Western counterparts.
The employment policy of the organization, which places more emphasis on skill than experience, supports the rising trust in Chinese educational establishments. Because China has historically lacked "hard-core" breakthroughs, Liang Wenfeng, the founder and CEO of DeepSeek, made it clear that "top talents are underestimated in China." These skills do exist and may produce ground-breaking work without the need for foreign degrees or training, as DeepSeek is now demonstrating.
2. A Break from Dependency on "Sea Turtle"
Known as "sea turtles" (海归), many of China's leading AI researchers, engineers, and scientists studied for decades at prestigious universities in the US, Europe, and other Western nations before returning to China. This was mainly due to the perception that domestic universities lacked the state-of-the-art research facilities found in the West.
This long-held belief is called into question by DeepSeek's growth. A thorough examination of its core personnel shows that the vast majority received their training in China, with very few having any academic experience abroad. Even more interesting is the fact that the majority of the professors who served as mentors for these researchers were graduates of Chinese universities, demonstrating that Chinese academic institutions can now produce elite talent independently of Western schooling.
The AI ecosystem in China will be significantly impacted by this. With access to cutting-edge research facilities, AI-focused degree programs, and abundant funding opportunities, Chinese universities are increasingly keeping their finest students rather than losing them to MIT, Stanford, or Oxford.
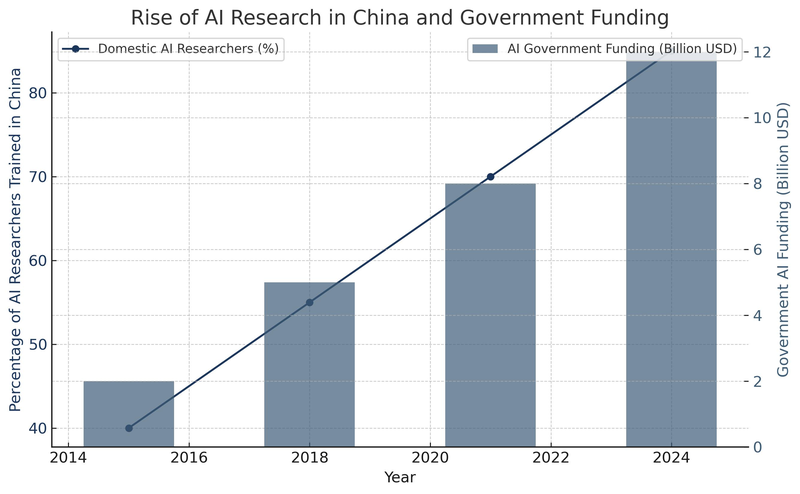
3. Government Spending on Education and AI
The Chinese government has made significant investments in DeepSeek for more than ten years, which has contributed to its success. China has spent billions on AI research, education, and industrial uses since it was declared a national priority in 2017. The nation has actively developed a top-tier AI ecosystem by:
establishing research facilities for AI at prestigious institutions.
providing yearly funding to thousands of PhD students studying AI.
promoting cooperation between academic institutions and internet behemoths like Baidu, Tencent, and Alibaba.
extending computer infrastructure to accommodate ambitious AI initiatives.
Chinese colleges have been able to move from being followers to leaders in AI research because to these efforts. Institutions like Peking University and Tsinghua University are now regarded as strong substitutes for Stanford or MIT in AI research, and the AI talent pipeline is no longer dependent on overseas training.
4. DeepSeek as a Sign of China's Independence in Innovation
In particular, U.S. technological limitations on China have contributed to DeepSeek's explosive growth. The goal of export prohibitions on cutting-edge AI processors and limitations on Chinese access to Western AI models was to impede China's technical advancement. Rather, they have spurred domestic innovation, forcing Chinese businesses and universities to create indigenous substitutes.
Similar to China's successful creation of the Tiangong Space Station and the BeiDou satellite navigation system despite being shut out of Western partnerships, DeepSeek has demonstrated that China is capable of producing top-notch AI models independently of American technology. The effectiveness and inventiveness of Chinese academics educated in domestic universities are demonstrated by the models' performance, even in the face of restricted access to powerful computer resources.
5. Chinese Universities' Increasing Reputation
Universities that taught DeepSeek's researchers are likewise becoming more well-known as its AI models become more well-known worldwide. Long regarded as two of China's best universities, Peking University and Tsinghua University are currently rising in the world rankings for AI research. These universities' reputations are greatly enhanced by the fact that DeepSeek's talent pipeline is virtually exclusively domestic, which draws in top students who might have otherwise thought about studying elsewhere.
With papers from colleges like Tsinghua and Peking often appearing alongside those from MIT and Stanford, China's universities have also been more represented at important AI conferences. This change demonstrates China's academic institutions' increasing legitimacy on the international scene.
6. Preserving Skill and Mitigating Brain Drain
The success of DeepSeek points to a larger shift in China's technical development strategy, one that emphasizes independence more. It is changing the career choices of China's most talented students by demonstrating that the country can produce world-class AI advancements. More young Chinese scientists are opting to remain in China, where they may contribute to innovative projects like DeepSeek, rather than feeling the need to study overseas in order to access possibilities for cutting-edge research.
The motivation for Chinese students to seek AI education in their homeland will only increase as more businesses emulate DeepSeek. The trend of sending top talent abroad for study and research is probably going to slow down as China's institutions continue to gain international recognition and the highest governmental levels promote the development of AI.
In conclusion, Chinese universities are entering a new era.
The achievement of DeepSeek demonstrates the maturity of China's academic and research institutions and goes beyond a single company's triumph. It has increased Chinese institutions' confidence in their capacity to attract and keep bright minds by proving that domestic talent can match the best in the world.
China's best universities are now regarded as independent innovation powerhouses rather than just stepping stones to universities abroad. A new age in which Chinese institutions are at the forefront of global AI research and technological growth is replacing the days of automatically sending China's best students overseas.
Similar Post
HE experts wary of STEM focus in immigration policy debate
Input
Modified
The UK's higher education sector, notably its STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) departments, confronts significant worries due to recent adjustments in immigration regulations. Despite warnings from academic and governmental agencies, the UK government has proven reticent to change these rules, even though there is a clear acknowledgment of their potential harmful impact on STEM provision. Universities that significantly depend on international students for both academic and financial support are alarmed by the tightening of visa requirements and the high application fees. There are concerns that the nation may jeopardize its own growth aspirations in high-tech industries and scientific innovation if the government doesn't change immigration laws or grant STEM talent exemptions. In order to avoid long-term harm to the STEM sectors, experts are advising the government to reconsider its immigration and higher education policy as the UK vies for top talent on a global scale.
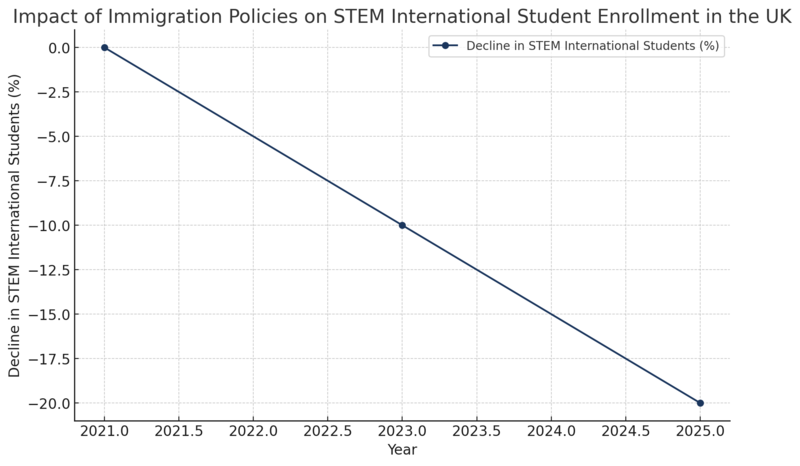
International cooperation has long benefited the UK's higher education system, as evidenced by the fact that many STEM programs depend on non-EU students for both their financial and technical support. Recent immigration reforms by the government, however, have sparked questions about these programs' long-term sustainability. Academics and business executives are particularly concerned about the proposed modifications to the skilled worker visas and the implementation of higher wage limits. The minimum wage threshold for skilled worker visas has been raised dramatically by the UK's new immigration regulations, which take effect in April. Potential foreign talent may be turned off by this, especially postgraduate students, young professionals, and researchers in early career stages in disciplines like science and technology. In addition to upsetting people's chances for a successful career, these changes have unintended consequences that may impede continued research and technology development in the UK. Furthermore, as the nation's reliance on foreign student fees for funding grows, universities with robust STEM offerings—such as postgraduate taught courses—may be disproportionately impacted by the new regulations.
In a recent report, the House of Lords Science and Technology Committee emphasized the dangers of these policies and urged the government to reconsider how restrictive immigration laws affect the UK's ability to compete in science and technology. The Committee is particularly concerned about the exorbitant fees for UK visas, which are currently among the highest in similar nations. International researchers and students may be deterred from selecting the UK as their destination by these growing expenses, which are exacerbated by the upfront payment of health levies. Although some UK leaders have admitted that foreign talent propels scientific and economic advancement, they have so far opposed meaningful reforms to immigration laws. The Committee has recommended that the UK adopt a more inclusive and flexible immigration system, similar to that of Australia, in order to draw in top-tier STEM talent and maintain the expansion of the country's innovation economy.
The government's position has made the discussion more divisive. On the one hand, experts contend that in order to continue to be a global leader, the UK needs to be flexible in luring talented individuals in domains such as artificial intelligence, engineering, and medical research. However, some commentators on higher education are concerned that STEM may be overemphasized at the expense of other important disciplines like the humanities, social sciences, and the arts. However, there is increasing agreement that the UK's goals for academic and technological advancement are not being met by the current immigration framework. The current challenge is striking a balance between the need to promote a thriving, globally competitive STEM sector and the requirement for effective immigration control. In the end, the UK's reputation as a center for innovation, research, and higher education may suffer long-term harm if the government does not address these issues. The UK's higher education sector, notably in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics), is concerned of immigration policies due to their potential to weaken the country's capacity to attract top international talent and maintain the viability of its STEM programs.
Several factors contribute to this concern:
Substantial Immigration fees: The UK government’s visa and immigration rules impose substantial up-front fees on students and researchers. This includes the substantial immigration health surcharge, which has increased by up to 58% since 2021, and the requirement for applicants to pay these fees upfront before they even enter the country. These expenses, which can reach tens of thousands of pounds for early-career researchers, discourage many from pursuing their studies or careers in the UK. The UK is now less competitive in the global talent competition as other nations have lowered their visa fees.
Impact on STEM Postgraduate Programs: Many STEM postgraduate courses, particularly at the master's and PhD levels, rely heavily on international students, who not only provide critical academic and research contributions but also help subsidize the teaching and research costs through their tuition fees. The UK's stringent immigration laws, such as the tuition fee freeze and the prohibition on dependents for postgraduate taught courses, have put a financial burden on universities and disproportionately harmed STEM programs, according to the House of Lords. Institutions face significant financial challenges as the number of international students declines, especially in expensive fields like STEM.
Lack of Government Flexibility: The government has resisted changing its policies in spite of cautions from the House of Lords and the higher education industry. While the government acknowledges that some STEM fields rely on international students for their survival, it has not yet taken substantial steps to ease restrictions. Proposed reforms, such as excluding international students from net migration statistics or easing the Tier 2 salary threshold for post-graduation work visas, have been rejected.
Global Talent Visa Concerns: While the Global Talent Visa is seen as a positive move, it has limitations in terms of eligibility, particularly for early-career researchers. The visa’s high costs and restricted eligibility criteria make it difficult for many talented individuals in STEM fields to benefit from it. The House of Lords has suggested expanding this visa or creating a new route specifically tailored to high-potential early-career researchers.
Competition from Other Countries: As the UK competes with other nations like the US and Australia for global talent, restrictive immigration policies put it at a disadvantage. In particular, countries like Australia have adopted more flexible visa systems that make it easier to recruit international talent, including tracking individuals through their immigration status, which the UK has not fully embraced.
Economic Impacts: The UK economy relies on a steady supply of STEM graduates to drive innovation and growth in key sectors like technology and engineering. The country's immigration policies, however, make it harder to attract and retain skilled workers in these areas. With a mismatch between the demand for STEM graduates and the supply of local talent, limiting the ability to bring in international experts could significantly harm the country’s competitiveness and growth prospects.
In summary, the UK’s current immigration policies are seen as a major hurdle for the STEM sector, both in terms of attracting international students and researchers and maintaining the financial stability of STEM programs at universities. The sector is urging the government to adopt more flexible and competitive visa policies to ensure the UK remains a top destination for global STEM talent.
Similar Post
Why STEM Majors Have Higher Tuition Fees: A Justified Cost
Input
Modified
STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) master’s programs are among the most expensive graduate degrees, often rivaling or surpassing MBA programs in tuition costs. With some programs exceeding $60,000 in total fees, many students wonder why these degrees come with such a high price tag. While it may seem excessive at first glance, the reality is that STEM education requires substantial investment in faculty, research infrastructure, and industry collaborations. Unlike business or humanities programs, where a classroom and textbooks might suffice, STEM fields demand state-of-the-art labs, cutting-edge computing resources, and highly specialized instructors who could otherwise be earning much more in private industry.
Despite the high costs, STEM graduate degrees remain one of the best financial investments due to their high return on investment (ROI). Many STEM graduates secure well-paying jobs quickly, with fields like artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and biomedical engineering offering six-figure starting salaries. Additionally, the strong global demand for STEM expertise means that tuition prices are unlikely to drop anytime soon. In this article, we break down why STEM master's programs are so expensive and why their cost is justified, covering everything from faculty salaries to research expenses and career prospects.

1. Higher Faculty Salaries in STEM Departments
- STEM professors, especially in fields like engineering, medicine, and IT, have higher salaries than those in humanities or social sciences.
- Professors often have industry experience, patents, and research projects that justify their compensation.
- Competition with the private sector forces universities to pay competitive wages to retain talent.
STEM professors are among the highest-paid faculty members in universities due to their expertise, industry demand, and contribution to research. Unlike humanities professors, many STEM faculty members have extensive industry experience and continue to engage in cutting-edge research, making them valuable assets to their institutions. Fields like artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and data science offer lucrative salaries in the private sector, meaning universities must offer competitive wages to attract and retain skilled educators.
Additionally, many STEM professors are involved in patent development, government-funded research, and consulting projects. Their work directly contributes to technological advancements and industry partnerships, which bring prestige and financial benefits to the university. However, these faculty members demand higher salaries due to their dual role as educators and researchers.
Since universities need to compete with the private sector for top-tier faculty, higher tuition fees for STEM majors help fund these salary demands. This ensures that students receive instruction from experienced professionals who are actively engaged in their fields, rather than from purely academic theorists.
2. Costly Laboratory and Research Equipment
- STEM education requires expensive lab facilities, equipment, and maintenance.
- High-tech fields like biotechnology, physics, and engineering demand continuous investment in new technology.
- Research opportunities for students also require significant financial backing.
One of the most significant contributors to high STEM tuition costs is the need for specialized laboratory facilities. Unlike humanities or business programs, which primarily rely on lecture halls and books, STEM programs require access to costly equipment such as spectrometers, supercomputers, and advanced medical devices. Maintaining these resources is not only expensive but also requires constant upgrades to keep pace with industry advancements.
For example, an engineering program may need wind tunnels for aerodynamics testing, while a biomedical program might require genome sequencing tools. These investments are crucial to ensuring that students gain hands-on experience with the same equipment they will encounter in their professional careers. Without continuous funding for such resources, STEM graduates would enter the workforce without the practical knowledge that employers expect.
In addition, universities invest heavily in student research opportunities, allowing them to participate in groundbreaking studies, publish papers, and contribute to technological innovation. These research programs, often funded by government grants and private corporations, still require substantial university support to cover operating expenses, further increasing tuition costs.
3. Smaller Student-to-Faculty Ratios and Personalized Education
- STEM programs often have lower student-to-faculty ratios due to lab-based courses.
- Individualized instruction, mentorship, and research supervision require more faculty members.
- Smaller class sizes provide better hands-on learning experiences.
Unlike large lecture-based courses in non-STEM fields, many STEM programs require smaller class sizes due to their interactive and experimental nature. In lab-based courses, a single professor may oversee a class of only 15–20 students, ensuring that each student receives personalized guidance and supervision. This is necessary for safety, practical learning, and ensuring that students master complex concepts effectively.
Additionally, research-intensive STEM programs require professors to mentor students closely on projects, theses, and experiments. This level of individualized instruction necessitates hiring more faculty members and teaching assistants, which raises operational costs for universities. Unlike humanities courses, where a professor can lecture to hundreds of students at once, STEM subjects require direct engagement and hands-on experience, making mass instruction impractical.
To sustain this high-quality education model, universities charge higher tuition fees to cover the costs of additional faculty, laboratory supervisors, and research assistants. The investment in smaller class sizes ultimately benefits students, ensuring they receive focused attention and a deeper understanding of complex scientific principles.
4. Industry Partnerships and Cutting-Edge Research
- STEM departments often partner with private industries, influencing curriculum and research.
- Universities fund state-of-the-art research to maintain industry relevance.
- These partnerships require ongoing investments in talent, facilities, and technology.
STEM fields evolve rapidly, and universities must stay ahead of technological advancements to remain competitive. Many STEM programs establish partnerships with leading corporations, allowing students to work on real-world projects, gain industry insights, and even secure internships before graduation. However, maintaining these relationships and offering industry-relevant coursework requires significant financial investment.
For example, universities that collaborate with companies like Google, Tesla, or Pfizer may need to set up dedicated research centers, purchase industry-grade tools, and provide specialized training for faculty. These partnerships often come with the expectation that universities will continue producing graduates equipped with cutting-edge skills, requiring continuous investment in faculty development, facility upgrades, and new research initiatives.
Although these collaborations benefit students by increasing employment opportunities and hands-on learning experiences, they also contribute to the rising costs of STEM education. Tuition fees help universities sustain these partnerships, ensuring that graduates remain competitive in the job market and are well-prepared for industry demands.
5. STEM Degrees Have Higher Earning Potential and ROI
- STEM graduates generally have higher starting salaries than non-STEM peers.
- The return on investment (ROI) justifies higher tuition fees.
- Strong job demand in tech, engineering, and healthcare provides career stability.
One of the strongest justifications for higher STEM tuition fees is the long-term financial return on investment. Graduates of STEM programs consistently earn higher starting salaries and experience greater job stability than those in non-STEM fields. Fields such as computer science, data science, and biomedical engineering have some of the highest-paying entry-level positions, making the upfront cost of education a worthwhile investment.
According to salary reports, STEM graduates often see an immediate return on their educational investment, with some earning six-figure salaries within a few years of entering the workforce. Additionally, the demand for STEM professionals continues to grow, ensuring strong job security and career advancement opportunities. Unlike fields with oversaturated job markets, STEM fields remain resilient in economic downturns, further validating the cost of education.
Higher tuition fees also reflect the significant value of the education received. Universities invest heavily in ensuring that their STEM graduates are equipped with industry-relevant skills, advanced technical knowledge, and practical experience. The financial benefits that students gain over the course of their careers far outweigh the initial costs, making the investment in a STEM degree well-justified.
Conclusion: STEM Tuition Fees Are a Necessary Investment
- High tuition fees support top-tier faculty salaries, advanced facilities, and hands-on learning.
- Industry partnerships and cutting-edge research drive innovation but require significant funding.
- Graduates benefit from strong job prospects, high salaries, and long-term career stability.
While STEM degrees come with higher tuition costs, they offer unparalleled educational quality, research opportunities, and career benefits. From ensuring access to experienced professors and cutting-edge laboratories to securing industry partnerships and high job placement rates, the costs associated with STEM programs directly contribute to students' future success. Ultimately, the investment in a STEM degree pays off, making the higher tuition fees both necessary and justifiable.
Similar Post
How To Use AI To Boost Your LL.M. Personal Statement
Input
Modified
Harness the power of AI to elevate your LL.M. personal statement! Tools like ChatGPT enhance language, generate ideas, and refine grammar, but they should never replace your unique voice and personal experiences. Relying solely on AI creates a generic, impersonal statement that fails to showcase what makes you stand out. Thus, prospective LL.M. students should exercise caution while using ChatGPT and other AI technologies to create their personal statements. Although these tools can be very helpful for improving language, coming up with ideas, or proofreading grammar, they shouldn't be used only to write the personal statement. This guide explains how to use AI effectively while avoiding common pitfalls, ensuring your application remains authentic and compelling.
Authenticity Is Essential
A candidate's distinct personality, experiences, and motivations are intended to be reflected in their personal statement. Beyond an applicant's grades, admissions staff want to know more about them. A lack of authenticity may result from writing the personal statement with artificial intelligence (AI) or from heavily altering it. Personal statements need to reflect genuine personality, experiences, and motivations. AI-generated content can sound generic or overly formal, losing the personal touch that admissions committees value in showcasing a candidate's true character and individuality.Presenting the statement in your own voice, which AI cannot imitate, is essential.
Possibility of detection
A personal statement that seems too general or lacking specifics may arouse suspicions because many admissions committees have methods to identify AI-generated content. Schools place a high value on authenticity and may reject AI-assisted content because of their unfavorable perception. Many law schools use tools to detect AI-generated content. A personal statement that lacks personal detail or sounds unnatural may raise red flags, potentially leading to suspicion of dishonesty or even rejection. The statement is weakened by an over-reliance on AI. Over-reliance on AI can deprive the personal statement of its uniqueness, even though it can assist with grammar checks, language improvement, and structural recommendations. Admissions committees prefer to see firsthand accounts and concrete instances that demonstrate the applicant's genuine beliefs, experiences, and driving forces. This richness is frequently absent from AI-generated text, which sounds more formal or general. Relying too heavily on AI can lead to a statement that lacks depth and nuance. Admissions teams are looking for detailed, reflective insights that showcase the applicant's specific experiences, goals, and motivations—qualities AI cannot fully capture.

Moral Issues
Since using AI to write large portions of application essays may be viewed as dishonest or similar to cheating, many educational institutions and application platforms advise against doing so. For example, content produced by AI might not adhere to the institution's standards for academic integrity. Using AI to generate significant portions of a personal statement may be seen as academic dishonesty or cheating. Many law schools explicitly discourage or prohibit AI use in application essays, as they want applicants to demonstrate their own critical thinking and writing abilities. Absence of Nuance Although AI tools can help with idea generation and language improvement, they frequently fall short when it comes to complex storytelling. AI cannot adequately handle a personal statement, which should thoughtfully and personally address your unique background, goals, and any potential shortcomings (such as poor grades or gaps in experience).AI tools may fail to capture subtle details or personal stories that would highlight why the applicant is suited for law school. Sensitive topics, such as explaining gaps in experience or addressing low grades, require a personal touch that AI cannot effectively provide. AI tools tend to produce generic, trite, or impersonal writing. Personal statements should stand out by offering unique, specific examples that showcase why the applicant is the right fit for the program. AI-generated content often lacks the creativity and personal connection necessary for an impactful statement. Additional Clarification Your Story in Your Statement: Candidates can discuss their goals, reasons for wanting to pursue an LL.M., and what makes them a special fit for the program in their personal statement. AI is unable to replicate your unique experiences, struggles, and victories. AI may propose general concepts like "justice" or "making a difference," for example, but it is unable to recount the details of a volunteer experience or a pivotal event in your life that led you to pursue a legal education. Telling these tales will help you stand out from the competition.
AI as a Tool, Not a Crutch
In certain situations, AI can be applied morally and successfully. For instance: Brainstorming: It can help you come up with concepts for possible experiences or themes. Structure: AI can offer suggestions on how to organize your statement, ensuring clarity and flow. Proofreading: It can assist in detecting grammar mistakes or helping with wording, but it should never replace your personal writing. Personal Accountability: Law schools expect applicants to submit work that accurately represents their thoughts and writing abilities. If an applicant is too reliant on AI, it risks showing a lack of personal accountability and effort, which might be seen as concerning when entering a rigorous academic environment like an LL.M. program. In Summary: Using AI tools like ChatGPT to assist in writing a personal statement can be valuable, but it should not replace the core of your application. Ensure that the voice, story, and content reflect your personal experiences and goals. AI can help fine-tune your writing, but the heart of the statement—your authentic narrative—must come from you.
Future Trends and Predictions Emphasis on Other Application Components
As AI-generated content becomes more prevalent, admissions offices may place greater emphasis on aspects of the application that are harder to replicate with AI, such as interviews, professional experience, and the cohesion of the applicant's overall story. This could lead to a shift in how applications are evaluated, with more focus on a candidate's lived experiences and less on the content of written statements alone. Ongoing Debate: The debate over AI's role in law school applications is far from settled. Some schools may revise their policies in the coming years, while others may continue to experiment with different approaches. As technology evolves, we can expect more nuanced and detailed guidelines from admissions offices in the future. How Applicants Should Proceed: Carefully Review Application Instructions: Given the variability in AI policies, applicants should carefully read the instructions for each law school they apply to, paying particular attention to AI usage clauses.
Draft an Organic Personal Statement
It remains wise to draft a genuine, human-written personal statement first. Even if AI is permitted, it’s still possible that using AI could make the statement less compelling. In many cases, AI assistance might only be helpful in editing an existing draft rather than generating an entirely new statement.

Use AI with Caution
If AI tools are used, applicants must ensure that their final statement retains a unique, authentic voice. AI should only be used as an editing tool, not as a substitute for genuine self-reflection and storytelling. In conclusion, the role of AI in law school applications is an evolving issue. Applicants should stay informed about the policies of individual schools and strive to maintain authenticity and integrity in their application materials, regardless of how AI is used.